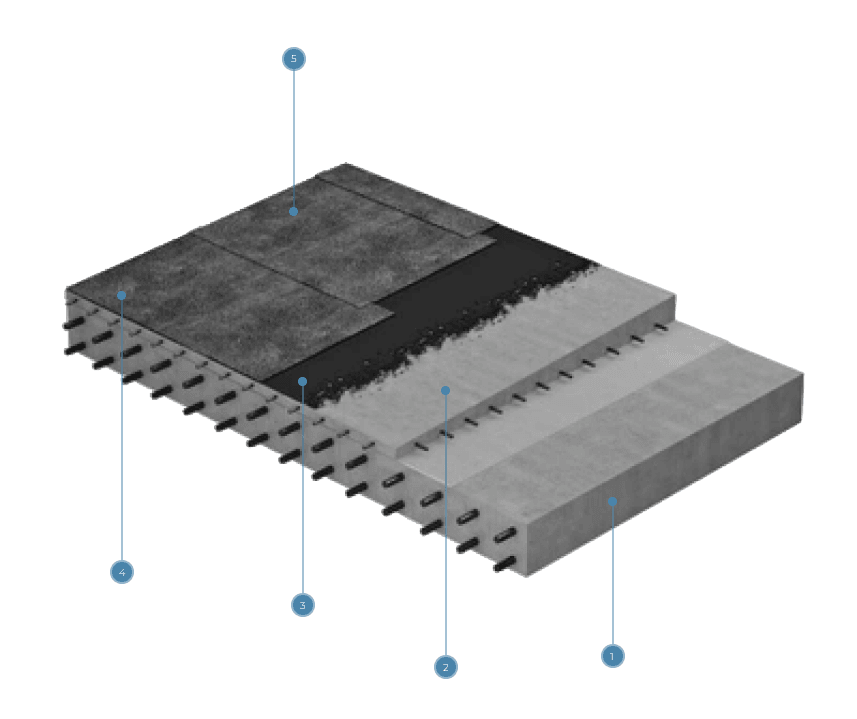
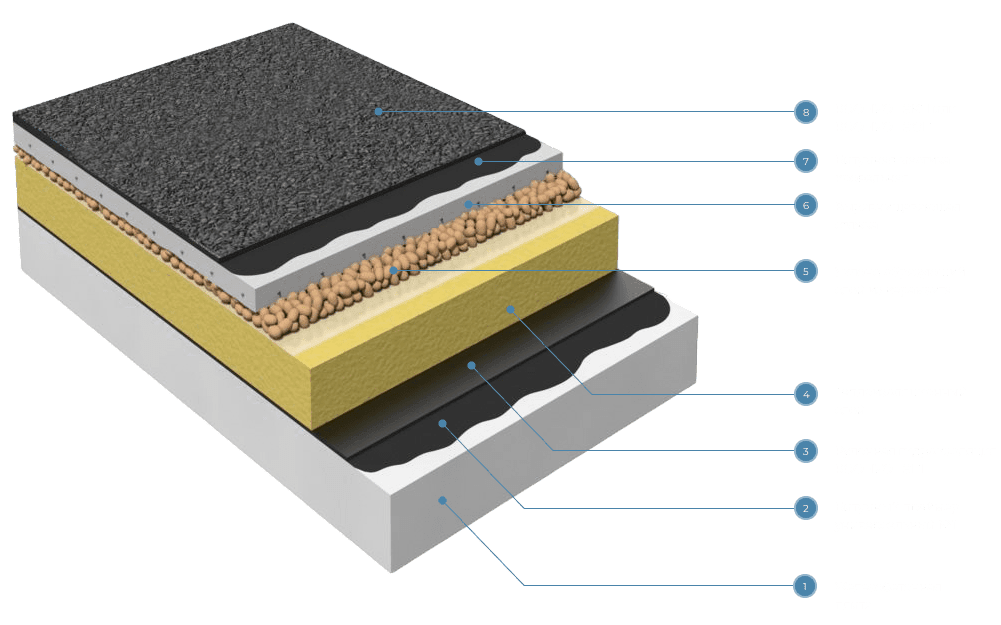
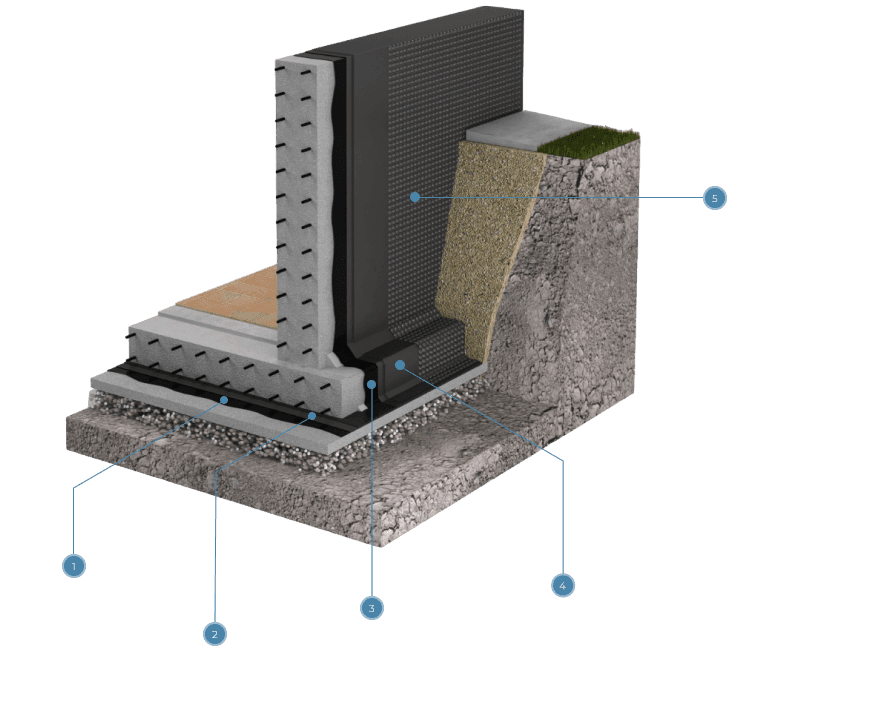
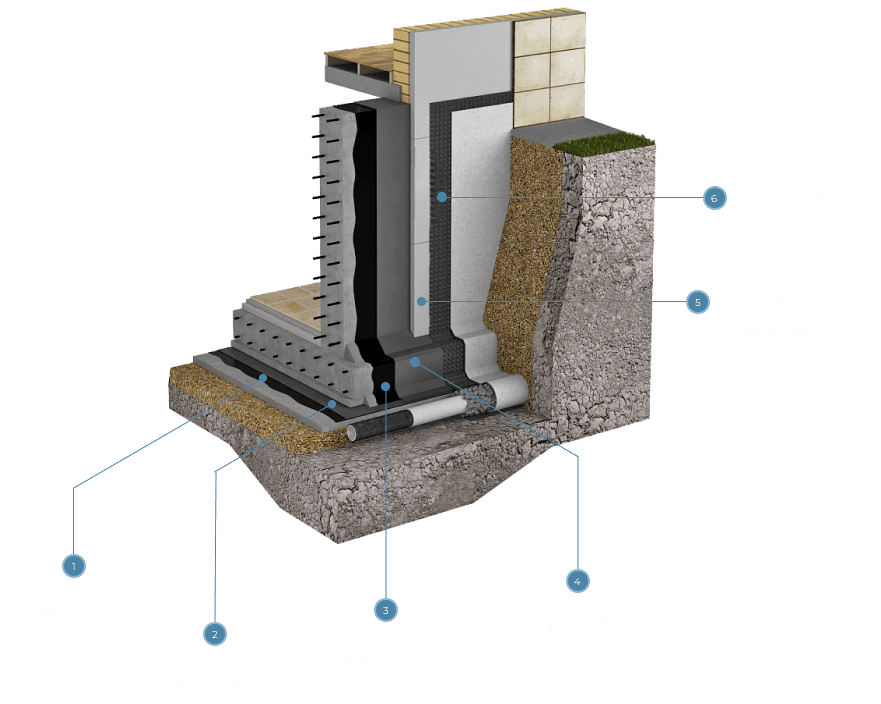
Bitumen is a highly viscous, thick substance derived from petroleum, widely used in construction and road works due to its unique physicochemical properties. The process of producing bitumen from petroleum is complex and multifaceted, involving several key processing stages. Below, we will examine the main stages that petroleum undergoes before transforming into bitumen.
- Extraction and primary processing of oil
Bitumen production begins with crude oil extraction, which is then transported to refineries. In the first stage, crude oil undergoes a primary refining process known as atmospheric distillation. The oil is heated to high temperatures in special columns, where it separates into several fractions based on their boiling points. Lighter fractions, such as gasoline and diesel fuel, are separated and removed, while heavier fractions, including fuel oil, remain at the bottom of the column.
- Vacuum distillation
After atmospheric distillation, the residual heavy fraction, called atmospheric residue, undergoes vacuum distillation. This process is carried out under reduced pressure, which allows the separation of even heavier oil components without their thermal decomposition. Vacuum distillation allows the isolation of vacuum gas oil and vacuum residue, the latter of which is the main raw material for bitumen production.
- Oxidation of bitumen (air blowing)
The vacuum residue undergoes further processing to obtain bitumen. One common method is oxidation, or so-called air blowing. This process involves passing air through a heated mass of vacuum residue at a temperature of 200 to 300 degrees Celsius. Oxidation helps increase the viscosity and improve the adhesive properties of bitumen, making it more resistant to water exposure and temperature fluctuations.
- Production of various types of bitumen
Depending on the processing technology and the additives used, different types of bitumen can be obtained, each with special characteristics and intended for various applications:
- Construction bitumen: This type of bitumen is used in road construction, roofing, and waterproofing materials. Special additives are used in its production to improve its adhesion and resistance to aging.
- Polymer-bitumen materials: During the production process, polymers are added to bitumen, which significantly improves its elasticity and heat resistance. Such materials are often used for road surfaces in areas with extreme climatic conditions.
- Emulsified bitumen: Obtained by mixing bitumen with water and emulsifiers, allowing it to be used at lower temperatures. Used in road construction, especially for laying thin pavements.
- Quality control and testing
After production, bitumen undergoes thorough testing and quality control. Parameters such as viscosity, softening point, water resistance, and adhesion are checked. This is necessary to ensure that the bitumen meets established standards and will effectively perform its functions under specific operating conditions.
- Packaging and transportation
After the bitumen has passed all stages of inspection, it is ready for packaging and transportation. Bitumen is usually transported in special tanks or barrels, which ensure its preservation during long-distance transportation. In some cases, bitumen is transported in a heated state to maintain its fluidity and facilitate the unloading process.
Total
Bitumen production from oil is a complex multi-stage process that involves crude oil refining, separation of heavy fractions, and subsequent processing to improve the properties of the final product. Thanks to various processing methods and additives, materials with unique characteristics suitable for a wide range of construction and road works can be obtained from bitumen. Each stage of production is important for obtaining high-quality bitumen, which will be a durable, reliable, and cost-effective material for various applications.